HK inno.N presents newest research findings of its new drug “K-CAB” at the DDW 2024
May 22, 2024
HK inno.N presents newest research findings of its new drug “K-CAB” at the DDW 2024, the world's largest gathering of GI professionals
HK inno.N releases new research results of K-CAB, a new P-CAB drug, at the DDW 2024.
▲ Analysis on the effects of long-term P-CAB or PPI administration on gastric physiology and small intestinal microbiome
▲ Comparison of K-CAB or PPI combination therapy in patients taking antiplatelet agents after PCI
HK inno.N expands its research portfolio with K-CAB, involving efficacy and safety of long-term use and combination therapies for cardiovascular diseases.
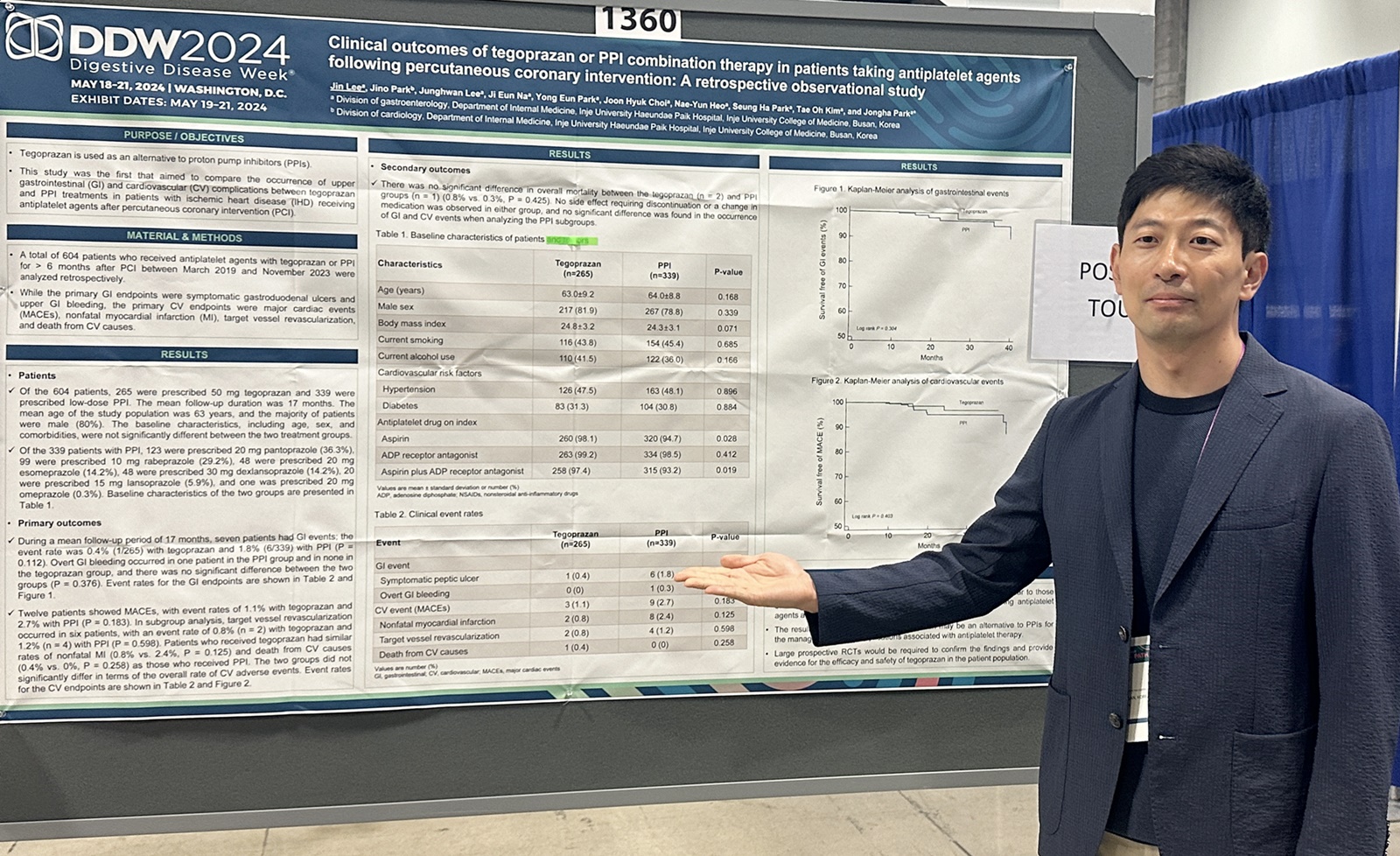
HK inno.N announced on 22th that it presented the latest research results of K-CAB, a new drug for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) at the Digestive Disease Week 2024 (DDW 2024) held in Washington, USA from 18th to 21th (local time).
HK inno.N released the results of two studies: ▲ a nonclinical study comparing the effects of long-term administration of P-CAB and PPI on gastric physiology and small intestinal microbiome; ▲ an investigator-initiated clinical study comparing the reduced incidence of upper gastrointestinal (GI) events and cardiovascular complications when K-CAB Tab. (tegoprazan) or PPI was concomitantly administered in patients taking antiplatelet agents after undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The results of these two studies were unveiled for the first time through poster presentations in this DDW conference.
Firstly, the nonclinical study on the 'effects of P-CAB and PPI on a change in gastric physiology and small intestinal microbiome after long-term use in experimental rats' was led by Professor Kim Yong-Sung at Wonkwang Digestive Disease Research Institute, Wonkwang University School of Medicine. In this study, "esomeprazole" as a PPI drug and "tegoprazan" and "vonoprazan" as P-CAB drugs were used.
After 4-week administration of P-CAB or PPI, P-CAB showed a more potent gastric acid inhibitory effect than PPI, but there was no significant difference between the two groups in delayed gastric emptying, hypergastrinemia, and small intestinal bacterial imbalance.
The second poster presentation was regarding the results of a study performed jointly by Professor Lee Jin and Professor Park Jong-Ha, Division of Gastroenterology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital. It is a retrospective study comparing the incidence of upper GI events and cardiovascular complications after K-CAB Tab. or PPI combination therapy in patients with ischemic heart diseases(IHD) who were taking antiplatelet agents after undergoing PCI.
K-CAB Tab. revealed similar study results to those for PPIs, recommended for administration in the guidelines, suggesting that K-CAB Tab. could be a therapeutic alternative to PPIs for the management of GI complications related to treatment with antiplatelet agents. In particular, this study is significant in that the therapeutic range of K-CAB has been expanded through combination therapy not only for digestive diseases but also for cardiovascular diseases.
"At this year's DDW, Korea's P-CAB drugs received special attention, demonstrating their values as Korea's new drugs in global P-CAB markets," said Dal-won Kwak, the CEO of HK inno.N, adding, “we affirm that K-CAB will expand its global position as the No.1 P-CAB even in the world beyond Korea by building up differentiated research portfolio and widening its therapeutic range as a leading product which has made its mark in the domestic P-CAB market."
K-CAB, the 30th domestic new drug, is a P-CAB class treatment for GERD which has created a P-CAB market in Korea. Since its launch, K-CAB has been ranked No. 1 in the domestic peptic ulcer drug market for four consecutive years, and last year, it recorded the outpatient prescription sales of KRW 158.2 billion, an all-time high in Korea. K-CAB has currently been sold in 45 foreign countries including the U.S., China, and Brazil, strengthening its global presence in international P-CAB markets. [END]
[Reference information]
- Study Titles
▶Poster - Comparison of long-term effects of P-CAB and PPI on gastric emptying rate, serum gastrin, and small intestinal microbiomes in rats
▶Poster - Clinical outcomes of tegoprazan or PPI combination therapy in patients taking antiplatelet agents following percutaneous coronary intervention : A retrospective observational study
- Glossary
▶PPI: Proton Pump Inhibitor
▶P-CAB: Potassium Competitive Acid Blocker
▶Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): A non-surgical procedure performed to widen narrowed coronary arteries, mainly to treat angina, myocardial infarction, etc. After PCI, thrombosis may occur, requiring treatment with antiplatelet agents, and to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding associated with this treatment, PPI treatment is recommended as specified in various domestic and overseas guidelines.
▶Ischemic heart diseases (IHD): A heart condition that causes an impaired blood supply, including unstable angina, acute myocardial infarction, and stable angina.
▶Hypergastrinemia: A condition with blood gastrin levels above the average normal level that may serve as a risk factor for gastric cancer and colorectal cancer.